Bundi language
The Bundi Language is a language first spoken by the Bundi tribe on Arbundia. It's the official language of the Arbundian Empire.
Phonology
The Bundi language has four vowels: ɐ, u, i, o̞ and 23 pulmonic consonants (used in words). There are 9 additional clicks and ejective consonants exclusively used only as conjunctions and sentence separators.
Bundi words are usually composed of one-consonant/one-vowel syllables and always end with a vowel. One exception is the vowel o̞ is only found at the beginning of words and forms a syllable without consonants. All the vowels are pronounced short, unless for the last vowel of a proper name. Pitch plays a major role, each vowel can be pronounced as one of eight discrete notes, however some combinations note/vowel are not used in standard Bundi speech. In phonetic notation this notes are written as number exponents over the vowel; for example the pitch of [i4] is lower than [i5].
Consonants are divided in 5 semantic categories. Changing a consonant from a category to another will change the meaning of the syllable. However the pronunciation of a consonant category depends on the place of the consonant from the end of the section. For example the first consonant category, is pronounced [n̥d] as the last syllable of a word, but is pronounced [ʀb] one place before last. The first consonant of a word containing a noun is silent (pronounced [ħ]) unless it's from category 5. The first consonant of a word containing a verb is always pronounced fully. Not all words strictly follow the consonants order, sometimes one or multiple virtual syllables are present (often as a result of word contraction), in these cases all the consonants preceding the virtual syllable are shifted in pronunciation.
Consonants
| Pulmonic | Place → | Labial | Coronal | Dorsal | Laryngeal | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manner ↓ | Bilabial | Labiodental | Alveolar | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal/epiglottal | ||||||||
| Nasal | m | n | ||||||||||||
| Plosive | ħp, p | ħb | n̥t | n̥d | ɡ | q | ʡ | |||||||
| Sibilant affricate | ts | dz | ||||||||||||
| Non-sibilant affricate | p̪fː | kxː | ||||||||||||
| Sibilant fricative | s: | z | ||||||||||||
| Non-sibilant fricative | ɸː | β, ħv | f | xː | ħ | |||||||||
| Trill | ʀb,ʀv | |||||||||||||
| Ejective | Stop | ʡʼ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affricate | t̠ʃʼ | ʈʂʼ | kxʼ | qχʼ | |
| Click | kǀ | kǃ | kǂ | kǁ | |
Morphology
The Bundi language is agglutinative, words are composed of various morphemes that can be isolated with a specific meaning (each syllable has nearly always a own meaning). The meaning is conveyed by the consonant category, the vowel and the pitch. Each word can be split in sections of maximum 6 syllables. Each one of this sections is a noun a verb or an adjective/adverb; the adjective/adverb always precedes the noun/verb to form a continuous word. So each word can be either the equivalent of a noun phrase or a predicate. In each section, each syllable will contribute to the meaning. For example a noun relating to an object will be composed by a root, giving its general nature, preceded by syllables giving characteristics relating to its size, material, shape, use...
Writing System
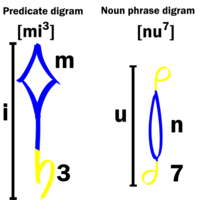
The Bundi language is written with the Arbundian script. This system was invented from scratch by Arbundi with the help of the Akavintu. It's an alphabetical system where each syllable is written by composing two symbols, forming a digram. The "Tail" conveys the pitch of the vowel, there is a symbol for each of the eight notes; the pronunciation of the vowel is determined by the height of the digram. The "Stalk" represents the consonant semantic category, with a different symbol for each, its pronunciation depends on its position from the end of the section.
Digrams in predicates are written with only one tail on the bottom of the stalk; on the other hand digrams in noun phrases are written with a tail at each end of the stalk, pointing at opposite sides. Words are written horizontally left to right or right to left, to emphasize proper noun phrases they are doubled with the second sequence mirrored. In the traditional script digrams of the same section of a word are written attached by their bottom tail, this facilitates pronunciation.
Virtual syllables are noted s, this symbol is never pronounced but it effects the pronunciation of the preceding consonants by "shifting" them, as if the word was a syllable longer.
The coordination separators are written between sentences as small symbols placed above the last symbol of the preceding sentence.
| Romanized [IPA] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position→ | Last | -1 | -2 | -3 | -4 | |
| Consonant
Category |
d | nd [n̥d] | rb [ʀb] | rv [ʀv] | g [g] | z [dz] |
| t | nt [n̥t] | hb [ħb] | hv [ħv] | / | sz [ts] | |
| n | n [n] | hp [ħp] | vf [β] | k [q] | s [z] | |
| m | m [m] | p [p] | f [f] | kh [kxː] | / | |
| f | / | pff [ɸː] | ff [p̪fː] | hc [ʡ] | ss [s:] | |
| Symbols | Vowel → | A | U | I | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note↓ | Relative digram height | ||||
| 1 | 1st | / | 4,5 | / | 7=o_ |
| 2 | 2nd | 2 | 4,5 | 6,5 | / |
| 3 | 3rd | 2 | 4,5 | 6,5 | / |
| 4 | 4th | 2 | 5 | 6,5 | / |
| 5 | 5th | 3 | 5 | 7 | / |
| 6 | 6th | 3 | 5 | 7 | / |
| 7 | 7th | 3 | 5 | 7 | / |
| 8 | 8th | 3 | / | 7 | / |
| Precedes equal sentence | Precedes important sentence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Key | Meaning [IPA] | Symbol | Key | Meaning [IPA] |
| # | # | Or | % | % | Although |
| + | + | But | * | * | If |
| : | : | So | ; | ; | Because |
| . | . | And | , | , | While |
| b | b | Ad Arbundi | |||
Grammar
Verbs
Verbs are built with a prefix that specifies the object and a suffix that specifies the the subject. The prefix is constructed with a consonant that depends on the person of the object (see table), the vowel is the last vowel of the object. The suffix is constructed similarly with a consonant dependent on the subject person and the last vowel of the subject. The tense is given by the pitch of the verb; all the syllables of a verb always have the same pitch, however associated adverbs will have an independent pitch.
| "Stalks" | Grammatical Person |
|---|---|
| d | Arbundi |
| t | Third absent |
| n | Second / third present |
| m | First singular |
| f | First global |
| Tail | Note↓ | Tense |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2nd | Remote past |
| 3 | 3rd | Far past |
| 4 | 4th | Near past ≈present |
| 5 | 5th | Likely future |
| 6 | 6th | Unlikely future |
| 7 | 7th | Infinite |
Nouns
Nouns always have a root suffix that gives the nature of the noun.
Sentences
Sentences always contain no more than one object, one subject and one verb. Sentences are constructed in the order Object-Verb-Subject, however for questions the order is Verb-Subject-Object and for any sentences where Arbundi is the subject the order is Subject-Object-Verb. To link sentences 9 different separators can be used. Each one having the function of a different coordination conjunction.