Eudiktya
| Eudiktya | |
| |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| Metatrophiria | |
| Distribution | |
| Miavegr | |
| Time Range | |
| 2 Ga - Present |
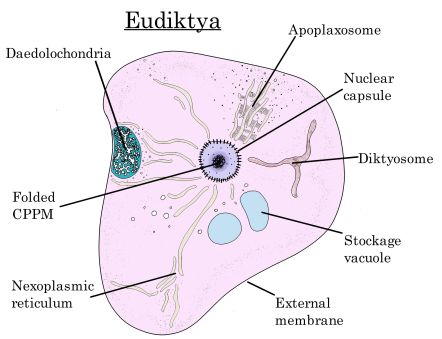
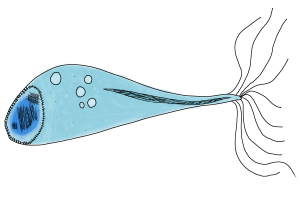
Eudiktya are a group of diversified unicellular or multicellular living organisms, they possess complex cells with organelles, their genetic material (CPPM) is protected by a pigment-protein capsule. They appeared around two billions years ago on Miavegr, they evolved in a large variety of lifeforms. They could be considered analogous to Earth's Eukaryota.
Organelles
Nucleus
The eudiktyan nucleus is delimited by a protein-pigment capsule. This shell protects the CPPM (the genetic material) from physical, chemical and radiative induced mutations. The nucleoplasm contains high concentrations of translating proteins (AT, CT) and amino acids. New proteins are synthesized in the nucleus , the nuclear capsule can open to let them through the rest of the cell. After the cell CPPM is replicated, the shell most often opens itself in two halves that migrate to the opposing poles of the cell.
Nexoplasmic reticulum
The nexoplasmic reticulum regulates transport and maturation of proteins. Moreover it is involved in the synthesis of new lipids, to expand the external membrane.
Diktyosome
The diktyosome is an organelle involved in the production and control of the cytoskeleton. It is essential for cellular movement and phagocytosis. This organelle recruits cytoskeletal proteins and polymerizes them correctly.
Daedolochondria
This organelle produces energy for the cell with aerobic respiration. It is composed by an external membrane and internal membrane. The internal membrane is extremely folded, this augments its surface area.
Apoplaxosome
This organelle is involved in most metabolic and anabolic functions, from amino acid synthesis to stockage glucid synthesis and food digestion. Long tubular membrane delimited compartments interconnected by glycoprotein polymers. This thread act as major enzymes. Some of the compounds produced inside the Apoplaxosome can be excreted by vesicles.
Vesicles/vacuoles
Vesicles are small spherical compartments, they can serve a large number of purposes (transport, excretion, digestion). Larger vacuoles mostly have a stockage or structural importance.
Reproduction
Eudiktyan cells are capable of sexual and asexual reproduction. Their cells can be haploid (one copy of the genetic material) or diploid (two copies of the genetic material). There is a large variability in reproductive cycles and the main stage can be either haploid or diploid, there can also be multiple stages).
Cellular division
In diploid cells the two CPPM copies are linked by Zirconium chelated to a Porphyrin from each CPPM. So the two copies are folded together inside the nuclear capsule. Diploid cells can divide two ways.
First, during a Dikaryophysis they can produce two diploid cells. When Zirconium Bonding Replicators (ZrBR), are not present, the two CPPM copies are replicated while still being attached. The two new copies are then bonded together by Porphyrin-Zr bridges. The two double genomes migrate into on half of the nuclear capsule. The two halves of the capsule separate and cell fully divides. Haploid cells can also have a Dikaryophysis division. In which case they produce two haploid cells.
Diploid cells can also divide in haploid cells, with a Tetraphysis division. First, ZrBR proteins are produced, which break the Porphyrin-Zr bridges and cause the two CPPM copies to separate. Each one of the copies is replicated. During this replication the Nuclear capsule fully breaks apart and the CPPM is fully unfolded. Because of this, some pieces of replicated CPPM can be exchanged between the two new copies. This recombination of the CPPM copies adds genetic variability as in Earth's eukaryote crossing-over. The four copies of CPPM are then folded and segregate in the four corners of the cell. The cell simultaneously splits apart in four and in each one of the child cells a new nuclear capsule covers the CPPM copy.
Gamy
Eudiktyan haploid cells can be gametes, which enable sexual reproduction. They can fuse to form a diploid child cell. The exact process is highly variable, but at the end the two CPPM are bonded by Porphyrin-Zr bridges. The resulting cell is a zygote.
Evolution
Eudiktya evolved around 2Gya ago. Their first
Phylogeny
| Eudiktya |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||